व्यायामात् लभते स्वास्थ्यं दीर्घायुष्यं बलं सुखं।
आरोग्यं परमं भाग्यं स्वास्थ्यं सर्वार्थसाधनम्॥
Your Spine determines your Lifeline !!!
The human spine, also known as the vertebral column or backbone, is a complex structure and a part of skeletal system. It is composed of individual vertebrae, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and muscles which carries out various function like movement, mechanical support and protection of the spinal cord.
Spinal health is critically important to overall well-being and longevity of an individual. For a better understanding, let us dive deep into the mechanics of the vertebral column.
Structure and function of Spine
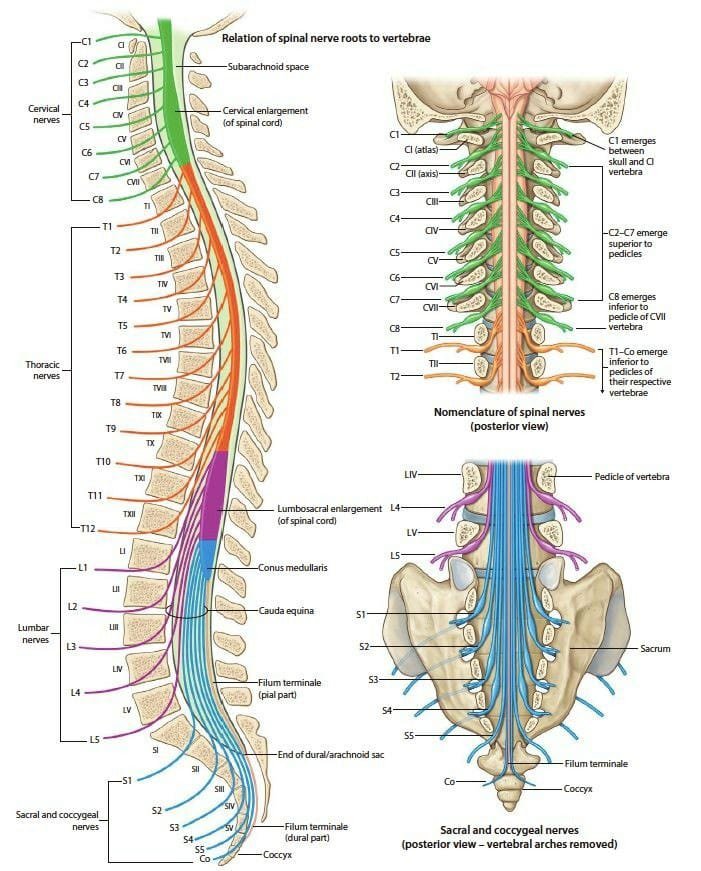
- Vertebrae: – These are 33 in number namely –
- Cervical Spine (Neck Region): Consists of 7 vertebrae (C1-C7). C1 (Atlas) supports the skull and allows nodding motion. C2 (Axis) enables rotational movement of the head.
- Thoracic Spine (Upper Back): Consists of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12). Each thoracic vertebra articulates with a pair of ribs.
- Lumbar Spine (Lower Back): Consists of 5 vertebrae (L1-L5). These are larger and stronger to support the weight of the upper body.
- Sacrum: Consists of 5 fused vertebrae (S1-S5). These form the back part of the pelvis.
- Coccyx (Tailbone): Consists of 4 fused vertebrae. These are vestigial structure with limited function.
- Intervertebral Discs –The human spine has 23 intervertebral discs.
- Structure: Located between adjacent vertebrae; composed of an outer fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus) and a gel-like center (nucleus pulposus).
- Function: Act as shock absorbers just like cushions, allow flexibility, movement, provide support and maintain spacing between vertebrae.
Curvatures of the Spine
- Cervical and Lumbar Lordosis: Inward curvatures of the spine.
- Thoracic and Sacral Kyphosis: Outward curvatures of the spine.
- Function: These curves help distribute mechanical stress during movement and provide balance.
Let’s see how they are distributed along the Spine:
- Cervical Spine (Neck Region) – There are 06 nos. intervertebral discs (located between the 7 cervical vertebrae).
- Thoracic Spine (Upper and Mid-Back) – There are 12 nos. intervertebral discs (located between the 12 thoracic vertebrae).
- Lumbar Spine (Lower Back) – There are 05 nos. intervertebral discs (located between the 5 lumbar vertebrae).
No intervertebral discs are present between the sacral vertebrae (which are fused to form the sacrum) or between the coccygeal vertebrae (which are fused to form the coccyx).
What happens when your Spine health is compromised ?
Here’s how spinal health can impact one’s life:
- Nervous System Function Impairment: -As the spine houses the spinal cord, poor spinal health, such as misalignment or disc herniation can compress nerves, leading to pain, numbness and impaired function in various parts of the body.
- Effect on Mobility and Quality of Life: – A healthy spine supports good posture and allows for flexible, pain-free movement. Issues like scoliosis, kyphosis, or lordosis can impair one’s mobility. Both acute and chronic back pain, sciatica can significantly reduce the quality of life, leading to decreased physical activity, which can further exacerbate health issues.
- Malfunctioning of Musculoskeletal System: –The spine’s health is intertwined with the health of the entire musculoskeletal system. Poor spinal health can lead to muscle imbalances, joint issues, and increased risk of injuries.
- Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: – Limited mobility due to spinal problems can lead to a sedentary lifestyle, thereby making an individual prone to more cardiovascular diseases.
- Impact on Mental Health: – Poor posture and bad spinal health can contribute to tension and stress, affecting mental well-being. Chronic spinal pain can lead to mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
- Internal Organ Innervation: –Nerves branching from the spinal cord innervate organs. An important nerve (vagus nerve) which is responsible for “rest and digest mode” is connected to all major systems of human body like digestive, respiratory, circulatory system etc. Spinal misalignments can interfere with this nerve supply, potentially impacting vital organ functioning.
How to take care of your Spine ?
Maintaining spinal health through proper posture, exercise, and ergonomic practices can contribute to overall longevity and a healthier life.
- Try to be mindful of your posture whether you are sitting, standing, eating or sleeping.
- Ensure workspaces and daily environments are ergonomically designed to reduce strain on the spine.
- Yoga can be a preventive as well as therapeutic care.Practicising regular yoga routine that tones and strengthen the back and core muscles can aid you in better management of spinal E.g Marjariasana, Bhujangasana, Shalabhasana, Naukasana, Dhanurasana, Ardhamatsendrasana etc
- Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity (either long hours of standing or sitting). Try to move around in between work-breaks.
- Use correct lifting techniques when lifting heavy objects to avoid any spinal injuries. E.g. Bending your knees and then lifting objects, holding heavy objects close to your core, distributing weights on both hands while carrying heavy things etc.
- Regular spinal check-ups can help detect and address issues early (if any), preventing long-term damage.
- Incorporating deep breathing and relaxation techniques as a habit is scientifically proven to release tension from nervous system and improves spinal health.
- Calcium, phosphorous and Vit D rich food can aid in maintaining bone health.
